Mythril is an open-source security analysis tool for EVM bytecode, courtesy of ConsenSys. It is also a component of their Security Analysis Service – Mythx. Mythril detects security vulnerabilities in smart contracts built for Ethereum and other EVM-compatible blockchains.
Vulnerabilities found by Mythril are reported with reference to the weaknesses listed on the Smart Contract Weakness Classification Registry (SWC Registry). I will use two entries from SWC Registry for the examples in this article:
- SWC-106 – Due to missing or insufficient access controls, malicious parties can self-destruct the contract.
- SWC-107 – One of the major dangers of calling external contracts is that they can take over the control flow. In the reentrancy attack (a.k.a. recursive call attack), a malicious contract calls back into the calling contract before the first invocation of the function is finished.
Install Mythril on Windows
> docker import mythril/myth
https://mythril-classic.readthedocs.io/en/master/installation.html
Get test files from github
Source code for these tests is on github : mythril-tests. Clone the repo locally and adjust the paths in the commands below to match your local environment.
Analyze a local smart contract
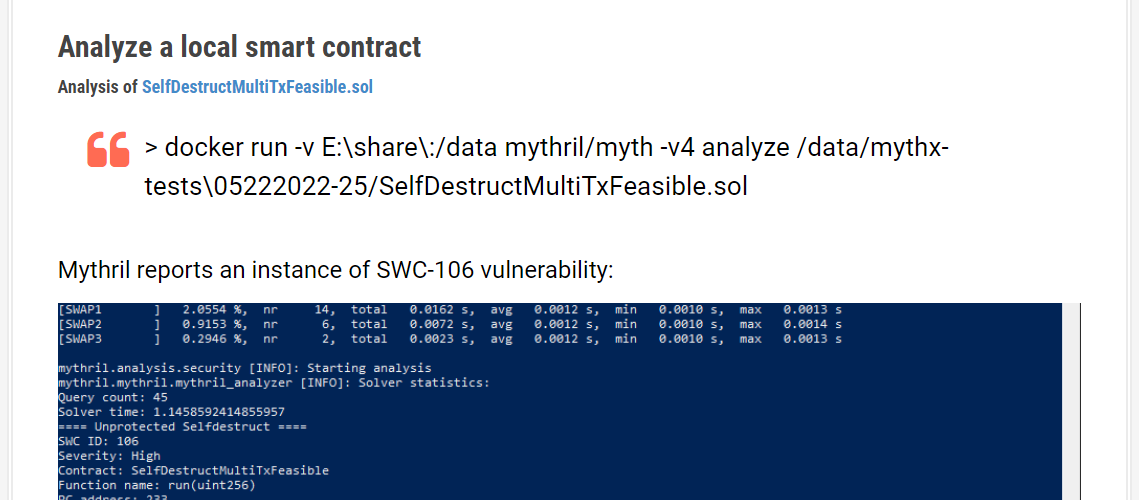
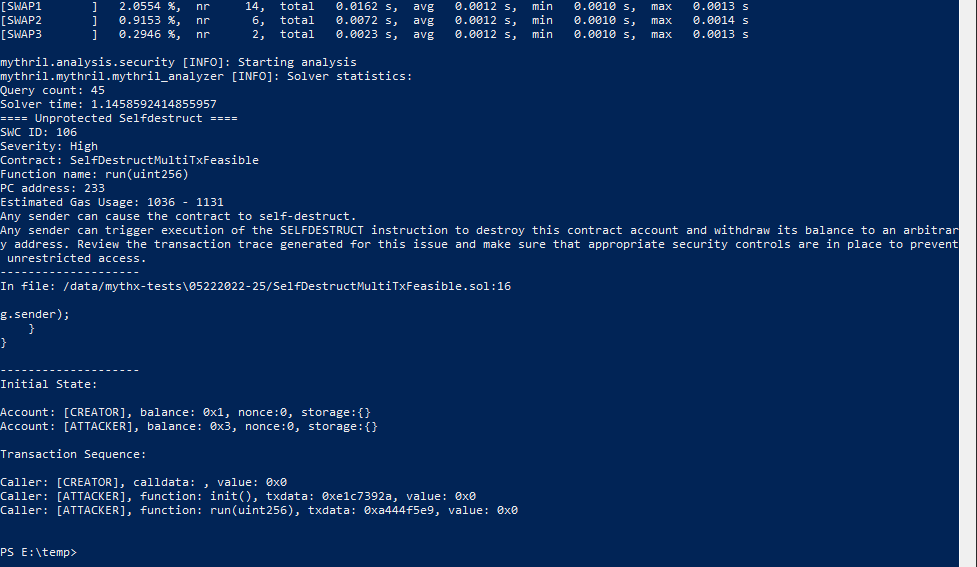
Analysis of SelfDestructMultiTxFeasible.sol
> docker run -v E:\share\:/data mythril/myth -v4 analyze /data/mythx-tests\05222022-25/SelfDestructMultiTxFeasible.sol
Mythril reports an instance of SWC-106 vulnerability:
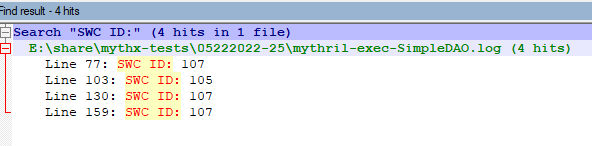
Analysis of SimpleDAO.sol
> docker run -v E:\share\:/data mythril/myth -v4 analyze /data/mythx-tests\05222022-25/SimpleDAO.sol
Mythril reports three instances of SWC-107 and one instance of SWC-105:
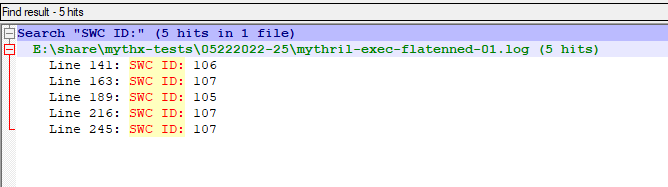
Analysis of a flatenned contract file
File containing the two test contracts returns five instances of vulnerabilities of both contracts:
> docker run -v E:\share\:/data mythril/myth -v4 analyze /data/mythx-tests\05222022-25/flatenned-01.sol
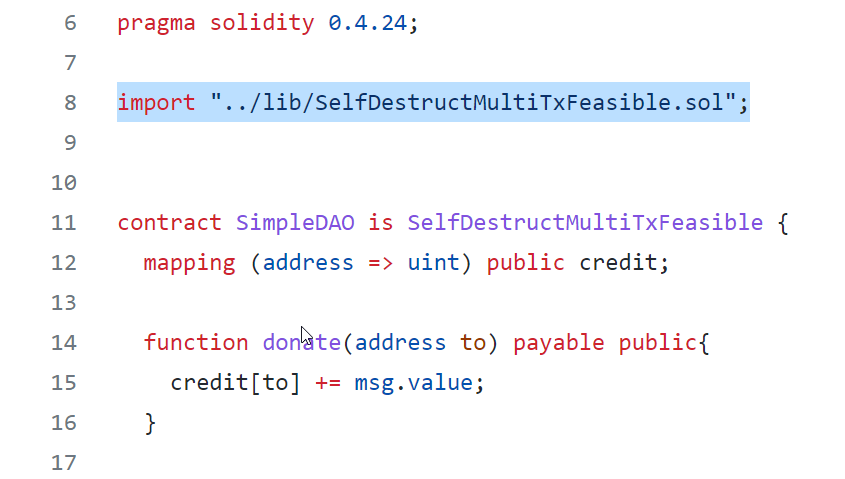
Analyze a contract with imported contract
Most smart contracts import other contracts to reuse functionality. You do not have to flatten the contracts into one file. Mythril can work with contracts with imports specified in them : SimpleDAOWithImport.sol
> docker run -v E:\share\:/data mythril/myth -v4 analyze /data/mythx-tests\05222022-26/SimpleDAOWithImport.sol
Analyze a contract with @OpenZeppelin style import
Mythril relies on solc for compiling contract source code. For @OpenZeppelin style imports, you have to specify –solc-json file containing remapping for solc to locate the referenced files : SimpleDAOWith-OzImport.sol
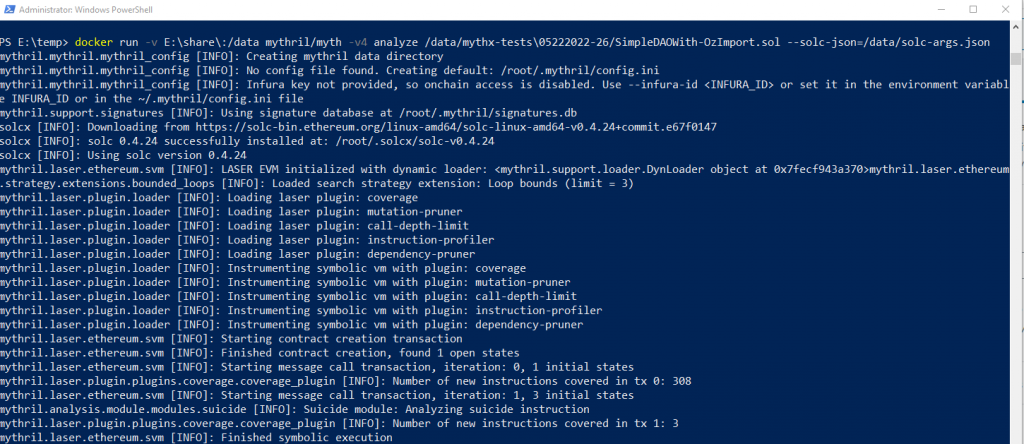
> docker run -v E:\share\:/data mythril/myth -v4 analyze /data/mythx-tests\05222022-26/SimpleDAOWith-OzImport.sol –solc-json=/data/solc-args.json
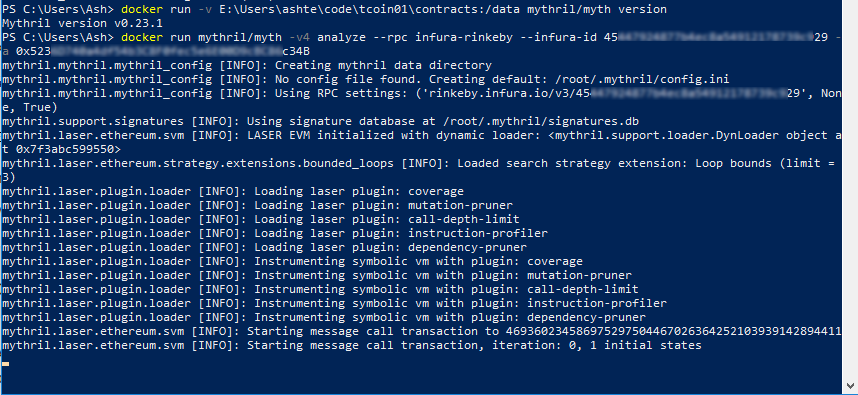
Analyzing On-Chain Contracts
Mythril can analyze contracts deployed on the blockchain directly. You do not need source code of the contract. Support for infura is built-in, you can also use custom RPC endpoint. Replace INFURA_ID with your Infura project id and CONTACT_ADDRESS with the address of your contract on the blockchain :
> docker run mythril/myth -v4 analyze –rpc infura-rinkeby –infura-id INFURA_ID -a CONTACT_ADDRESS